pH & Alkalinity
- Rick Fuller
- Oct 8, 2016
- 1 min read
Updated: May 15, 2022
pH and Alkalinity Relationships
The following two graphics are intended to provide a handy reference describing pH and alkalinity relationships. The source of this information is the excellent textbook from Nalco.
Source: Nalco Company. "The Nalco Water Handbook." Third Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2009.
pH Relationships
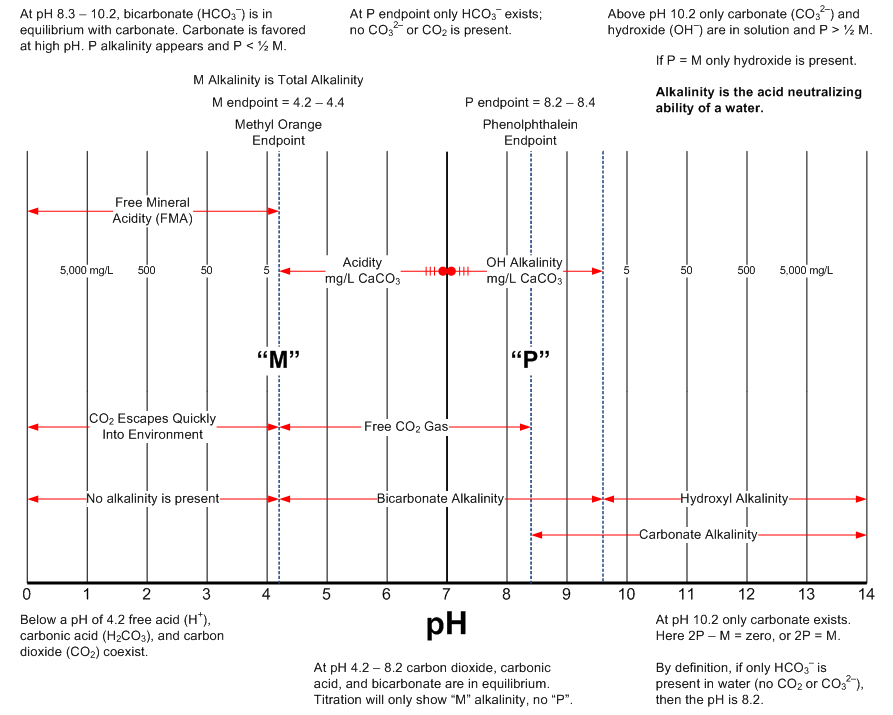
Alkalinity Relationships

You can download a PDF of these graphics by clicking below. If you want to reuse the images, and please feel free to do so, you might want to download the PowerPoint (.pptx file) which will allow you to more easily copy and past a higher quality graphic.
Alkalinity of a Water
The alkalinity in water is the result of mineral salts containing carbonate, bicarbonate, and hydroxide anions, with calcium and magnesium as the positively charged cations (counterions). Knowing the pH of water without a knowledge of the total alkalinity results in an incomplete understanding. Two water samples with identical pH but different alkalinities will respond very differently to the addition of acid. The higher the alkalinity in the water the more resistant that water will be to a change in pH with the addition of acid.

